Superelevation
(Created page with "The "superelevation" or the slope of rails in curves is proposed from now on in T:ANE. Here is the example of a machine launched to 80 kph in a curve of 500 meters of beam. ...") |
|||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
In France, the superelevation does not have to exceed 16 cms in standard gauge way and 10 cms in metrics. | In France, the superelevation does not have to exceed 16 cms in standard gauge way and 10 cms in metrics. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == '''Mode of calculation in T:ANE''' == | ||
| + | |||
| + | To proceed to the calculations, download the spreadsheet [http://1drv.ms/1NUaCsF here]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the left column, seize the '''minimum radius of curvature''' that can know your network, a maxi speed and choose the gauge (standard or metric). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Observe the parameter Superelevation (SE) calculated. If it exceeds 6.3 inch in standard gauge or 3.94 in metrics, it is necessary to decrease the maxi speed (according to French standards). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The parameters p1 and p2 then obtained can apply to all the curves of your network, whathever is their radius of curvature, since the maxi speed will not exceed the one that you seized in the spreadsheet. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:12.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | An example: | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the spreadsheet, you seize the values beam = 150 ft, speed = 55 mph and standard gauge. And you obtain a superelevation = 5 in, p1 = 43.73 and p2 = 0.089 radians. | ||
Revision as of 01:49, 8 November 2015
The "superelevation" or the slope of rails in curves is proposed from now on in T:ANE.
Here is the example of a machine launched to 80 kph in a curve of 500 meters of beam. Its slope has to be 4 ° to resist the centrifugal force and not not wear out prematurely the outer rails.
However, the implementation of the superelevation in T:ANE is little transparent for the moment. Here is thus a small guide who will supply you all the necessary elements.
In T:ANE, the superelevation is adjusted by means of two parameters. We reach it by the panel "rail", and " advanced mode "
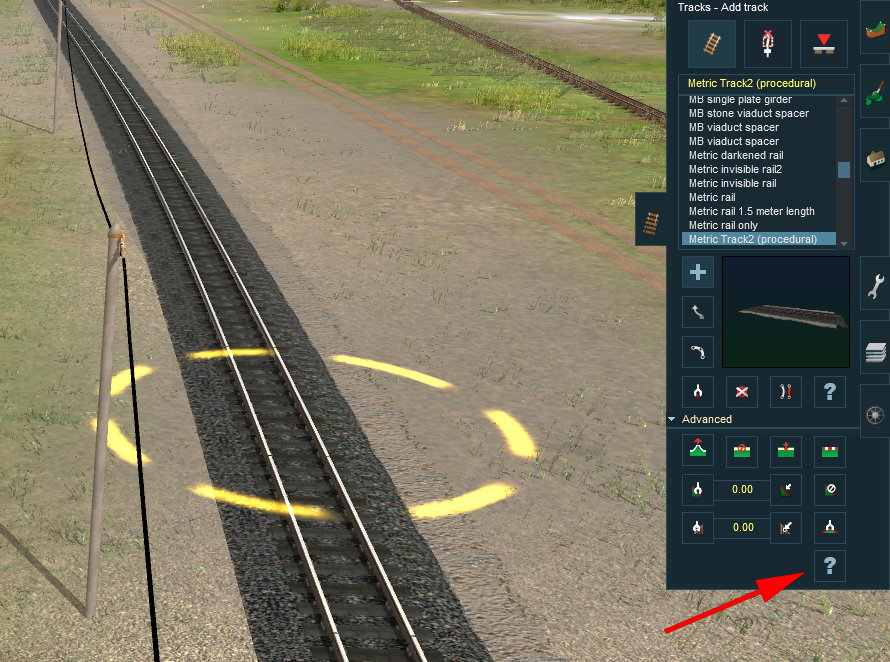
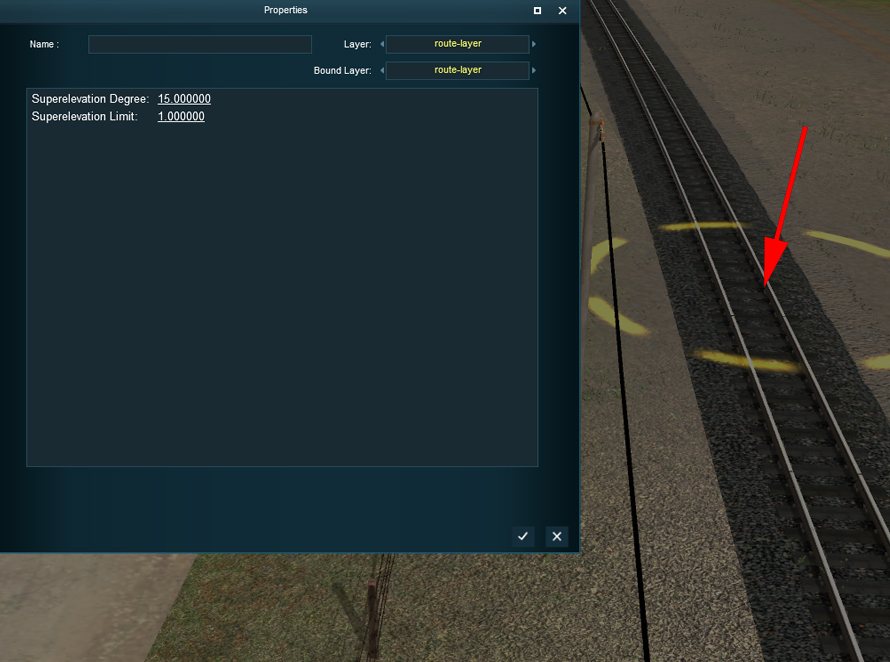 By clicking a summit of spline of track, we reveal both parameters to be served:
By clicking a summit of spline of track, we reveal both parameters to be served:
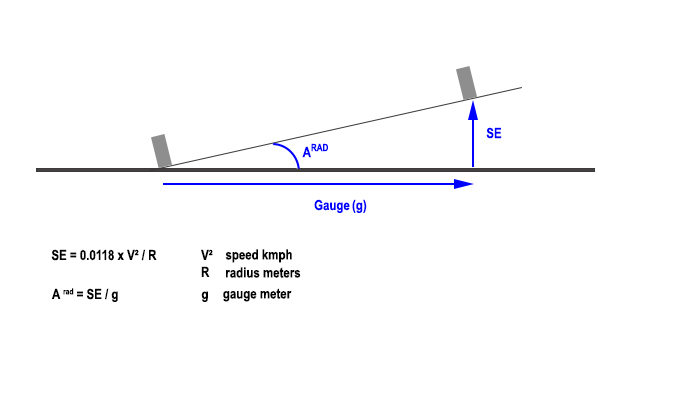
Superelevation : short definition
The Superelevation is the height which takes the outside rail compared with the internal rail in a curve.
It is calculated as the plan below shows it:
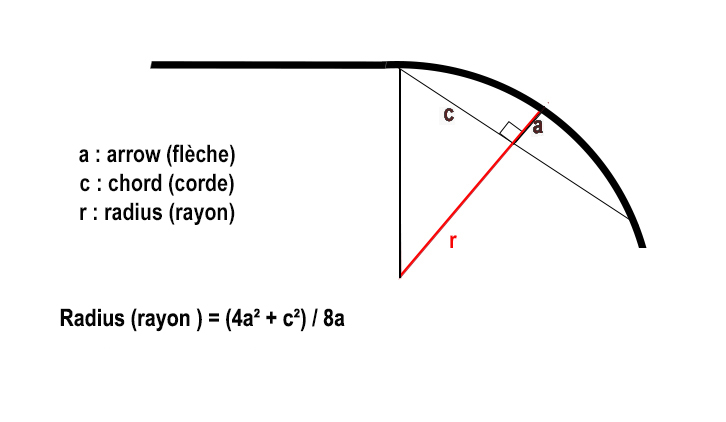
If, to calculate the superelevation, the beam of the curve is unknown, it can be calculated by measuring the arrow and the chord of the curve:
Every country has its own standards of superelevation. We find them rather easily on the internet.
In France, the superelevation does not have to exceed 16 cms in standard gauge way and 10 cms in metrics.
Mode of calculation in T:ANE
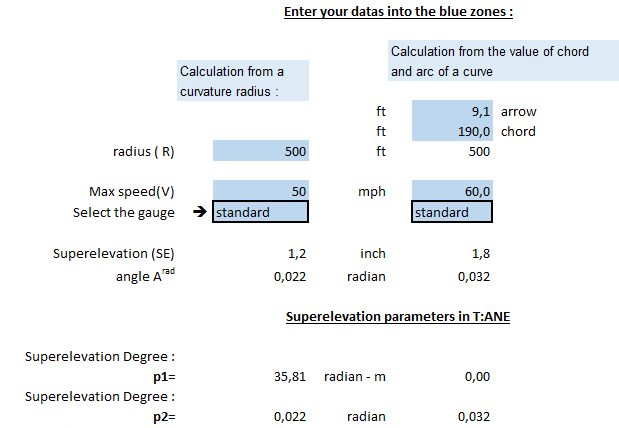
To proceed to the calculations, download the spreadsheet here.
In the left column, seize the minimum radius of curvature that can know your network, a maxi speed and choose the gauge (standard or metric).
Observe the parameter Superelevation (SE) calculated. If it exceeds 6.3 inch in standard gauge or 3.94 in metrics, it is necessary to decrease the maxi speed (according to French standards).
The parameters p1 and p2 then obtained can apply to all the curves of your network, whathever is their radius of curvature, since the maxi speed will not exceed the one that you seized in the spreadsheet.
An example:
In the spreadsheet, you seize the values beam = 150 ft, speed = 55 mph and standard gauge. And you obtain a superelevation = 5 in, p1 = 43.73 and p2 = 0.089 radians.